
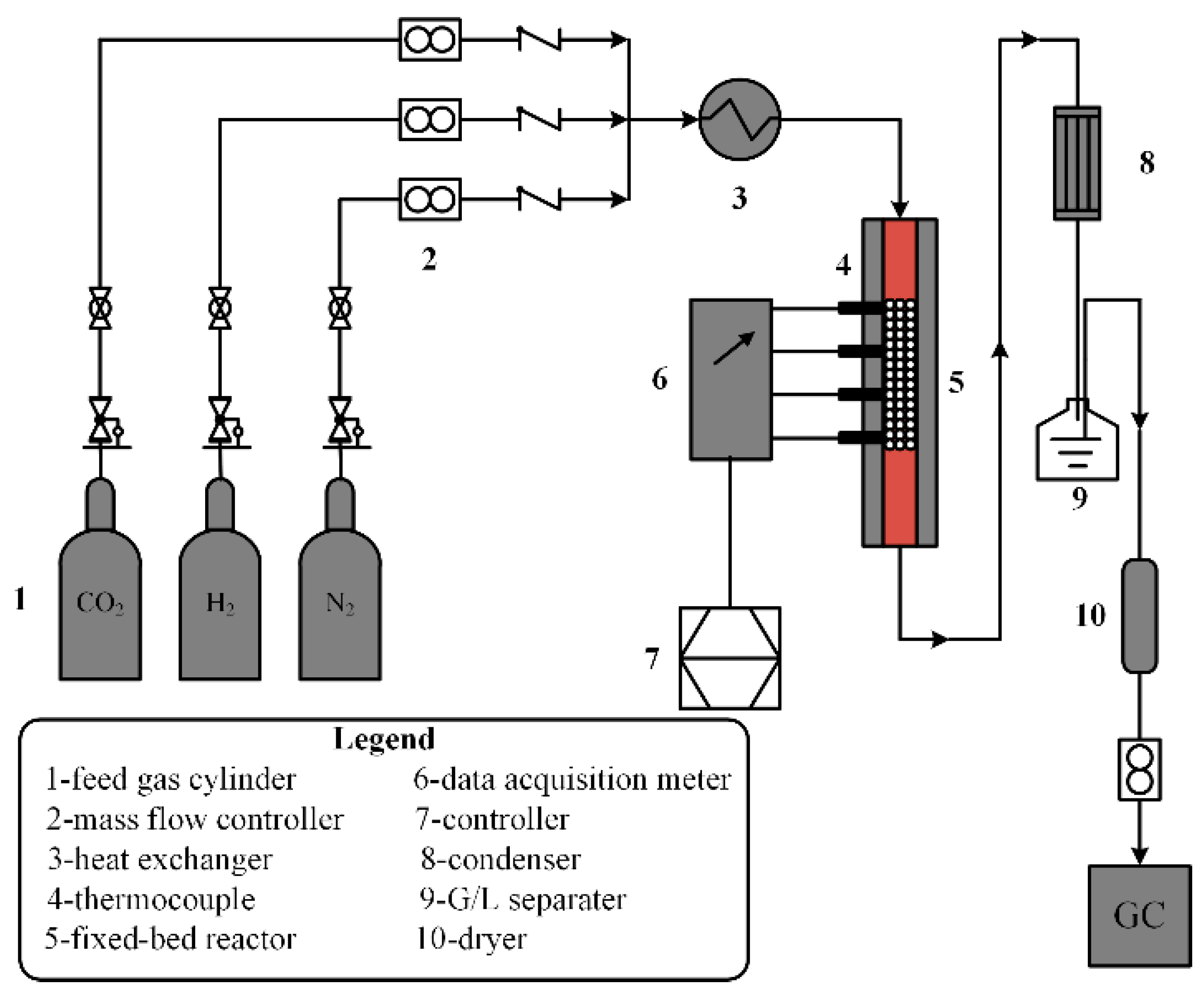
The threshold is obtained by using the statistics of the image. A thresholding step is incorporated in order to limit the number of potential target pixels. Then the filtered output is subtracted from the original image to enhance the potential targets. The raw image is first filtered by max-mean/max-median filter. Subsequently, anti-mean and anti-median operations result in good performance of detecting targets against moving clutter. In this paper, we investigate the usefulness of Max-Mean and Max-Median filters in preserving the edges of clouds and structural backgrounds, which helps in detecting small-targets. al., is one of the promising algorithms in this are. Triple Temporal Filter reported by Jerry Silverman et. The focus of research in this area is to reduce the false alarm rate to an acceptable level. However, the difficulties of detecting small-targets arise from the fact that they are not easily discernable from clutter. There are many algorithms reported in the open literature for detection and tracking of targets of significant size in the image plane with good results. “Our results on the thermodynamic arrow of time might also have stimulating consequences on the cosmological arrow of time,” say Micadei and co, hinting that similar correlations may be responsible for the universe’s initial conditions.This paper deals with the problem of detection and tracking of low observable small-targets from a sequence of IR images against structural background and non-stationary clutter. That has important implications for our understanding of time and its relationship to entanglement and entropy. “We observe a spontaneous heat flow from the cold to the hot system,” say the team. When the nuclei are entangled, the correlation places extra limits on the way the particles behave, resulting in a kind of engine that drives heat energy in the opposite direction. It is this phenomenon that Micadei and co have exploited to create the unique set of initial conditions that allow time to run backwards. Entanglement is the strange quantum process in which two quantum particles share the same existence. And the key is to entangle the nuclei in advance. In the new experiment, Micadei and co have observed the opposite. When one nucleus is hotter than the other, heat naturally flows from the hot one to the colder one.
The team can control the temperature of both nuclei by selectively heating them using nuclear magnetic resonance. And by listening to the radio signals emitted by the nuclei, the physicists can work out how the quantum states of the nuclei evolve.Īt the same time, the carbon and hydrogen nuclei are in thermal contact, meaning that heat energy can flow from one to the other. Physicists then use radio pulses to flip one or both spins, causing them to become correlated or entangled. The idea is to align the nuclei using a strong magnetic field. This creates a perfect playground for quantum physicists, who are able to manipulate the nuclear spins of single carbon and hydrogen nuclei using a technique called nuclear magnetic resonance. Chloroform-CHCl 3-consists of a single carbon atom, a single hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms. The exotic new system is a mixture of chloroform dissolved in nail polish remover, or acetone. The work raises the possibility of a new generation of devices in which the arrow of time runs backwards.
In their experiment, the arrow of time runs in reverse, allowing them to observe a cold object heating up a hotter one. Today, Kaonan Micadei at the Federal University of ABC in Brazil and a few pals have built such a system for the first time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
